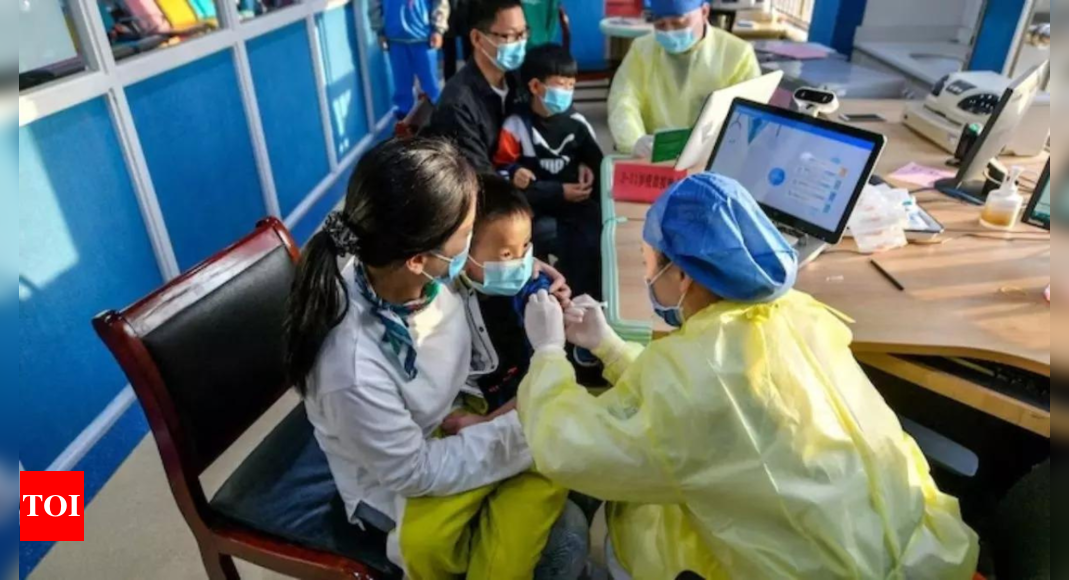
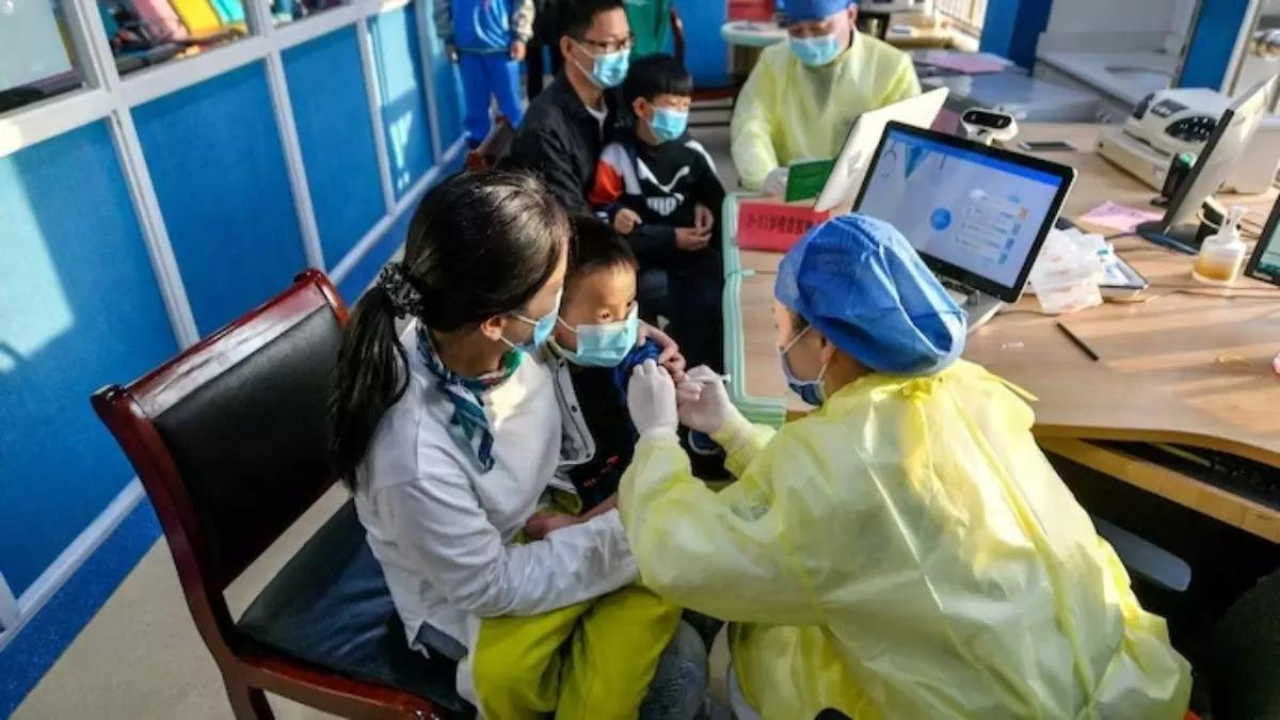
Chinese health authorities have not detected any unusual or novel pathogens and provided the requested data on an increase in respiratory illnesses and reported clusters of pneumonia in children, the World Health Organization (WHO) said on Thursday.
The WHO had asked China for more information on Wednesday after groups including the Program for Monitoring Emerging Diseases (ProMED) reported clusters of undiagnosed pneumonia in children in north China.
As per the rule, China responded to the WHO within 24 hours. The WHO had sought epidemiologic and clinical information as well as laboratory results through the International Health Regulations mechanism.
The data suggests the increase is linked to the lifting of COVID-19 restrictions along with the circulation of known pathogens like mycoplasma pneumoniae, a common bacterial infection that typically affects younger children and which has circulated since May.
Influenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and adenovirus have been in circulation since October.
The agency does not advise against travel and trade as they have been monitoring the situation with authorities.
No unusual pathogens have been detected in the capital of Beijing and the northeastern province of Liaoning.
Chinese authorities from the National Health Commission held a press conference on Nov. 13 to report an increase in incidence of respiratory disease.
Both China and the WHO have faced questions about the transparency of reporting on the earliest COVID-19 cases that emerged in the central Chinese city of Wuhan in late 2019.
The U.N. health agency had also asked China for further information about trends in the circulation of known pathogens and the burden on healthcare systems. The WHO said it was in contact with clinicians and scientists through its existing technical partnerships and networks in China.
WHO China said it was “routine” to request information on increases in respiratory illnesses and reported clusters of pneumonia in children from member states, such as China.
The global agency decided to issue a statement on China to share available information, as it received a number of queries about it from media, WHO China said in an emailed statement.
The ProMED alert was based on a report by FTV News in Taiwan that came out on Tuesday.
Undiagnosed pneumonia was not mentioned at last week’s press conference, according to a transcript, but one speaker said everyone felt like there had been an increase in respiratory illnesses this year compared with three years ago.
The speaker said that global monitoring for mycoplasma pneumoniae had been at a low over the past three years and outbreaks were cyclical, occurring every three to seven years.
‘Seasonal surge’
The rise in respiratory illnesses comes as China braces for its first full winter season since it had lifted strict COVID-19 restrictions in December. Many other countries saw similar increases in respiratory diseases after easing pandemic measures.
“It is just a relatively large seasonal surge, perhaps partly due to chance and partly because there’s a bit of ‘immunity debt’ from the lesser winter surges in the last three years,” said Ben Cowling, an epidemiologist at Hong Kong University.
China’s National Health Commission did not immediately respond to a request for comment.
On Thursday, it published an interview with the state media agency Xinhua in which it advised parents what to do and mentioned that big hospitals were receiving a large number of patients and waiting times were long. It did not comment on the WHO notice.
Since mid-October, the WHO said northern China had reported an increase in influenza-like illness compared with the same period in the previous three years.
It said China had systems in place to capture information on trends in illness incidence and to report that data to platforms such as the Global Influenza Surveillance and Response System.
In recent days, media in cities such as Xian in the northwest have posted videos of hospitals crowded with parents and children awaiting checks.
Some social media users have posted photos of children doing homework while receiving intravenous drips in hospital.
The WHO said that while it was seeking additional information, it recommended that people in China follow measures to reduce the risk of respiratory illness.
Measures included vaccination, keeping distance from sick people, staying at home when ill, getting tested and medical care as needed, wearing masks as appropriate, ensuring good ventilation, and regular hand-washing, it said.
The WHO had asked China for more information on Wednesday after groups including the Program for Monitoring Emerging Diseases (ProMED) reported clusters of undiagnosed pneumonia in children in north China.
As per the rule, China responded to the WHO within 24 hours. The WHO had sought epidemiologic and clinical information as well as laboratory results through the International Health Regulations mechanism.
The data suggests the increase is linked to the lifting of COVID-19 restrictions along with the circulation of known pathogens like mycoplasma pneumoniae, a common bacterial infection that typically affects younger children and which has circulated since May.
Influenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and adenovirus have been in circulation since October.
The agency does not advise against travel and trade as they have been monitoring the situation with authorities.
No unusual pathogens have been detected in the capital of Beijing and the northeastern province of Liaoning.
Chinese authorities from the National Health Commission held a press conference on Nov. 13 to report an increase in incidence of respiratory disease.
Both China and the WHO have faced questions about the transparency of reporting on the earliest COVID-19 cases that emerged in the central Chinese city of Wuhan in late 2019.
The U.N. health agency had also asked China for further information about trends in the circulation of known pathogens and the burden on healthcare systems. The WHO said it was in contact with clinicians and scientists through its existing technical partnerships and networks in China.
WHO China said it was “routine” to request information on increases in respiratory illnesses and reported clusters of pneumonia in children from member states, such as China.
The global agency decided to issue a statement on China to share available information, as it received a number of queries about it from media, WHO China said in an emailed statement.
The ProMED alert was based on a report by FTV News in Taiwan that came out on Tuesday.
Undiagnosed pneumonia was not mentioned at last week’s press conference, according to a transcript, but one speaker said everyone felt like there had been an increase in respiratory illnesses this year compared with three years ago.
The speaker said that global monitoring for mycoplasma pneumoniae had been at a low over the past three years and outbreaks were cyclical, occurring every three to seven years.
‘Seasonal surge’
The rise in respiratory illnesses comes as China braces for its first full winter season since it had lifted strict COVID-19 restrictions in December. Many other countries saw similar increases in respiratory diseases after easing pandemic measures.
“It is just a relatively large seasonal surge, perhaps partly due to chance and partly because there’s a bit of ‘immunity debt’ from the lesser winter surges in the last three years,” said Ben Cowling, an epidemiologist at Hong Kong University.
China’s National Health Commission did not immediately respond to a request for comment.
On Thursday, it published an interview with the state media agency Xinhua in which it advised parents what to do and mentioned that big hospitals were receiving a large number of patients and waiting times were long. It did not comment on the WHO notice.
Since mid-October, the WHO said northern China had reported an increase in influenza-like illness compared with the same period in the previous three years.
It said China had systems in place to capture information on trends in illness incidence and to report that data to platforms such as the Global Influenza Surveillance and Response System.
In recent days, media in cities such as Xian in the northwest have posted videos of hospitals crowded with parents and children awaiting checks.
Some social media users have posted photos of children doing homework while receiving intravenous drips in hospital.
The WHO said that while it was seeking additional information, it recommended that people in China follow measures to reduce the risk of respiratory illness.
Measures included vaccination, keeping distance from sick people, staying at home when ill, getting tested and medical care as needed, wearing masks as appropriate, ensuring good ventilation, and regular hand-washing, it said.
Denial of responsibility! Swift Telecast is an automatic aggregator of the all world’s media. In each content, the hyperlink to the primary source is specified. All trademarks belong to their rightful owners, all materials to their authors. If you are the owner of the content and do not want us to publish your materials, please contact us by email – swifttelecast.com. The content will be deleted within 24 hours.