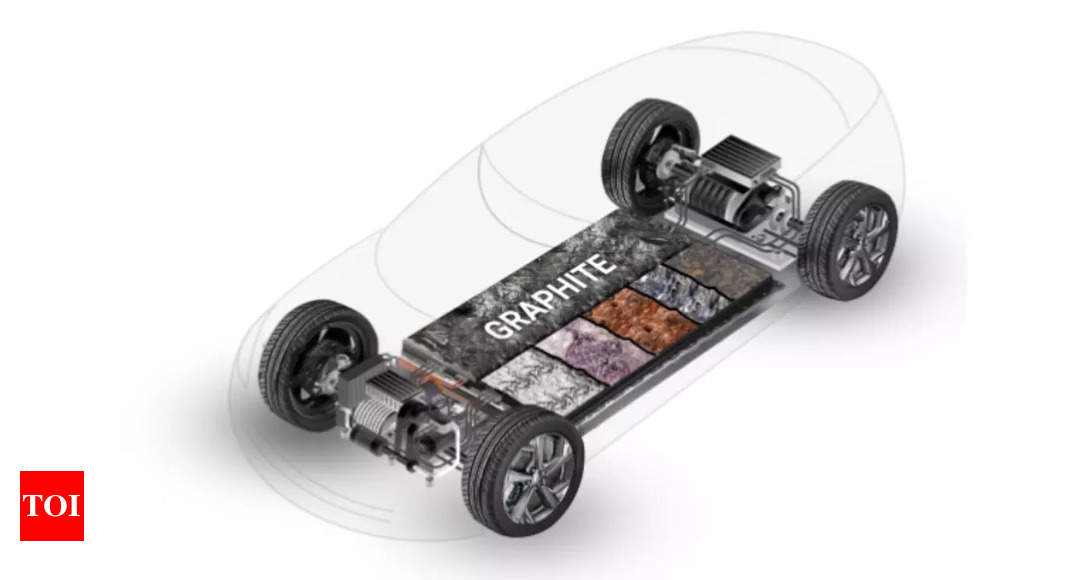
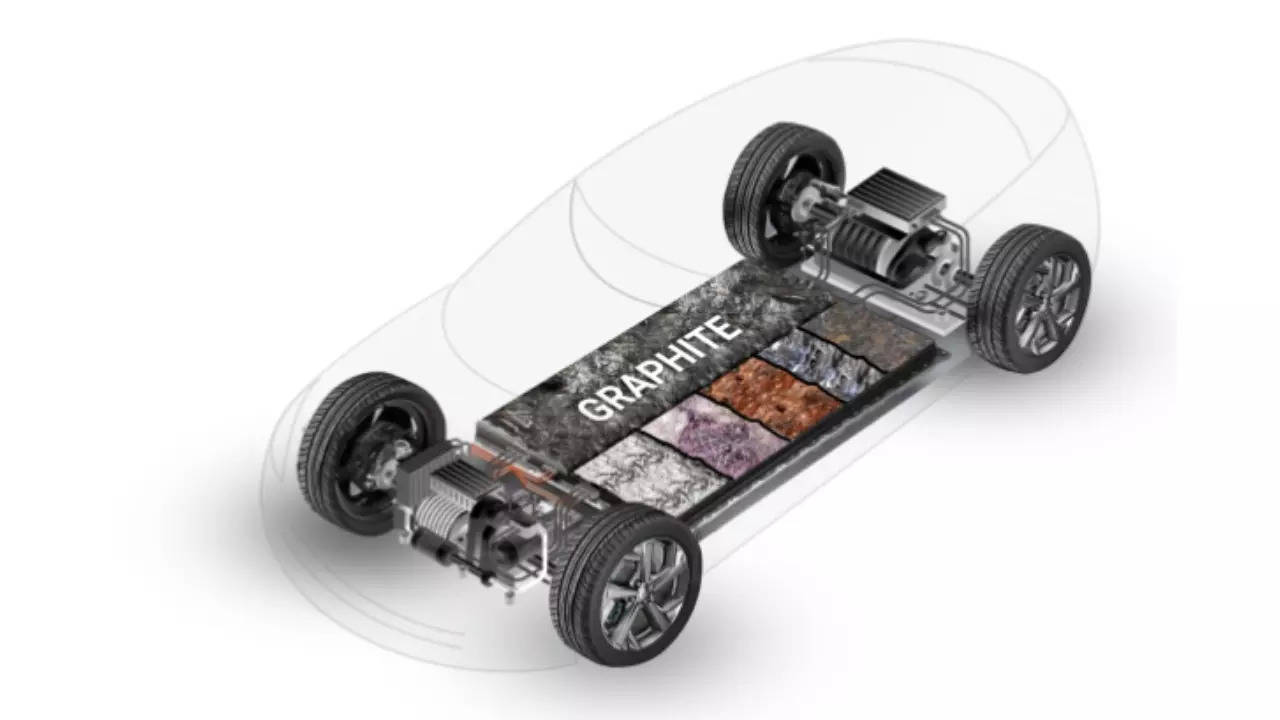
The battery market in India is emerging as a formidable force. Estimated to soar from USD 7.20 billion in 2024 to USD 15.65 billion by 2029, it is an industry on the rise. What’s compounding this growth is the rapid adoption of Electric Vehicles (EVs) with India earmarking a USD 47.71 million investment for battery energy storage systems.As renewable energy takes centrestage in the country’s environmental strategy, the capabilities of our energy storage systems will greatly influence India’s potential to become a leader in decarbonization.
While we have made significant strides in EVs, there is a need to prioritize the development of domestic next-generation, high-capacity batteries to secure a stable and steady power supply. These should meet the demand and promote India’s self-reliance, while laying the foundation for advanced research into diverse battery technologies, including the processing of battery materials. Research and development (R&D) efforts in this area should focus on improving battery performance, safety, longevity, and most importantly sustainability.
Empowering India through R&D
A strategic emphasis on the research and development sector is imperative for India to excel in the battery manufacturing ecosystem. Without a concerted strategy, the nation would encounter various challenges, including a fragile supply chain, diminished affordability, and external dependency, necessitating intermittent intervention through artificial support measures. For example, as the usage of lithium-ion battery cells expands across automotive, stationary storage, aerospace, and other sectors, there is a growing need to enhance their safety. While occurrences of lithium-ion cell accidents are exceedingly rare, they can occur under conditions of mechanical, thermal, or electrical stress or abuse. To mitigate this risk, it is essential to establish a robust research and development infrastructure which is capable of acquiring consumer insights and integrating real-time feedback into the development process to enhance overall quality.
MG Comet long-term Review: The perfect city car or an expensive toy? | TOI Auto
When discussing the research and development of next-generation advanced battery materials, there are several key areas that demand primary focus.
The initial stride toward establishing a resilient infrastructure for battery materials involves attaining energy sustainability, a decisive element in mitigating the carbon footprint. This can be realized through comprehensive research into resource, water, and energy circularity. An optimized circular approach minimizes resource wastage while concurrently enhancing durability and value. By leveraging captive feedstock and procuring raw materials, we can actively promote resource circularity within battery development. Concurrently, initiatives in water circularity mitigate fresh water consumption, emphasizing the utilization of treated wastewater and energy circularity reduces energy consumption by harnessing recovered waste gases. Moreover, the production of synthetic graphite anode materials, with a concerted emphasis on mitigating Global Warming Potential (GWP), assumes significance in achieving sustainability, given that the manufacturing of battery materials is identified as the primary source of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in lithium-ion batteries for automotive applications. Fuelled by technological advancements in the country, researchers and developers can discern and refine the most promising battery materials for diverse applications. They accomplish this by employing sophisticated scientific modelling and simulation methodologies.
Strategy to catalysing growth of Next-Gen battery materials
Working with all stakeholders in the supply chain: This essentially requires developing battery manufacturing workflows that employ a broad range of analysis techniques to ensure product performance and safety. Battery manufacturing employs diverse analysis methods like X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, and wet-chemistry approaches to ensure raw material and production stage quality. These assessments yield abundant data, encompassing outcomes, instrument metadata, and calibration data, emphasizing the requirement for precise documentation and availability to sustain an effective and regulatory-compliant production process. All these activities can be supported by providing the necessary support to lab prototypes in order to make them viable for indigenous testing.
Meticulous testing of liquid and pellet density, ash content, and moisture content: This is vital to ensure the integrity and quality of battery materials. It is essential to evaluate single pouch cells to ascertain their discharge capacity, efficiency, and material spring-back characteristics. Thorough testing of anode materials for battery properties, including reversible capacity, initial cycle efficiency, charging/discharging rate, and energy density, across various cell formats such as coin-cell, pouch cell, and multi-layer pouch cell, can yield an optimized battery performance and reliability.
Advancing government’s commitment to electric mobility: Present indicators suggest that lithium-ion technology will maintain its prominence in the battery market for the foreseeable future. Realizing these objective mandates will also require government deliberation so that stakeholders throughout the value chain are aligned with the nation’s overarching vision. A targeted emphasis on research and development holds the potential to diminish reliance on imported cell components.
The road ahead
The global battery market is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.8% from 2023 to 2030. Collaborative efforts between stakeholders, including industry partnerships and interdisciplinary research, will be key to accelerating the commercialization of breakthrough technologies. These investments will help meet the growing demand for energy storage solutions and advance sustainable development goals. The time is ripe to invest in research and create an environment for exploration that can enhance India’s position in the global market and meet future energy demands sustainably.
Disclaimer: Views and opinions expressed in this article are solely those of the original author and do not represent any of The Times Group or its employees.