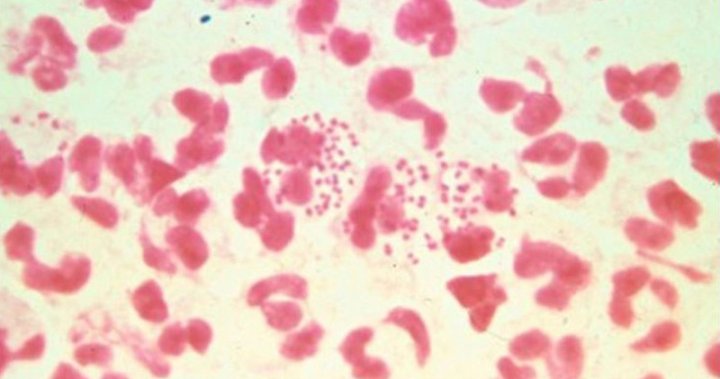
As gonorrhea rates increase in Canada, health officials are warning that the infection is becoming more resistant to antibiotics, potentially leading to untreatable cases. The World Health Organization (WHO) has reported growing treatment failures for gonorrhea in several countries, including Canada. Gonorrhea, a common STI, is usually easily treated with drugs like ceftriaxone. However, a strain of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, the bacteria that causes gonorrhea, has developed resistance to ceftriaxone and other antibiotics like penicillin.
Dr. Ameeta Singh, an infectious disease specialist at the University of Alberta, stated that gonorrhea rates have been increasing globally and in Canada for many years. The Public Health Agency of Canada (PHAC) also expressed concern over the increasing rates of gonococcal infection, the possible emergence of untreatable gonorrhea in Canada, and the prevalence of the infection among adolescents and young adults.
The symptoms of gonorrhea vary, and many individuals, particularly females, may have no symptoms. Common symptoms in men include a burning sensation when urinating, discharge from the penis, itching, and swollen testicles. In women, symptoms are often mild and non-specific, resembling a bladder or vaginal infection. Untreated cases of gonorrhea can have severe consequences, such as infertility and the spread of infection to other organs.
Gonorrhea is the second most commonly reported STI in Canada, and rates have almost tripled from 2010 to 2019. The rise in antibiotic-resistant gonorrhea is believed to be the main reason for this increase. While the use of two antibiotics, ceftriaxone and azithromycin, as a treatment strategy has been effective in some regions, others have seen higher resistance levels.
The development of antibiotic resistance occurs when genetic mutations in the bacteria make them less susceptible to the effects of the antibiotic. When a person with gonorrhea is treated with antibiotics, some resistant bacteria may survive, multiply, and pass on their resistance genes over time. Resistance organisms for gonorrhea are primarily arising in Asia, and cases of multi-drug-resistant gonorrhea in Canada are often acquired through sexual contact or travel.
The WHO has set targets to reduce new cases of gonorrhea globally, but combating the growing threat of drug-resistant strains requires comprehensive efforts in education, prevention, testing, and treatment. The availability of rapid tests and vaccines, like those used for meningitis prevention, could be crucial in preventing and controlling the spread of gonorrhea.